|
Ordering information |
|||
|
Name |
Cat. No. |
Vol. |
Scheme |
|
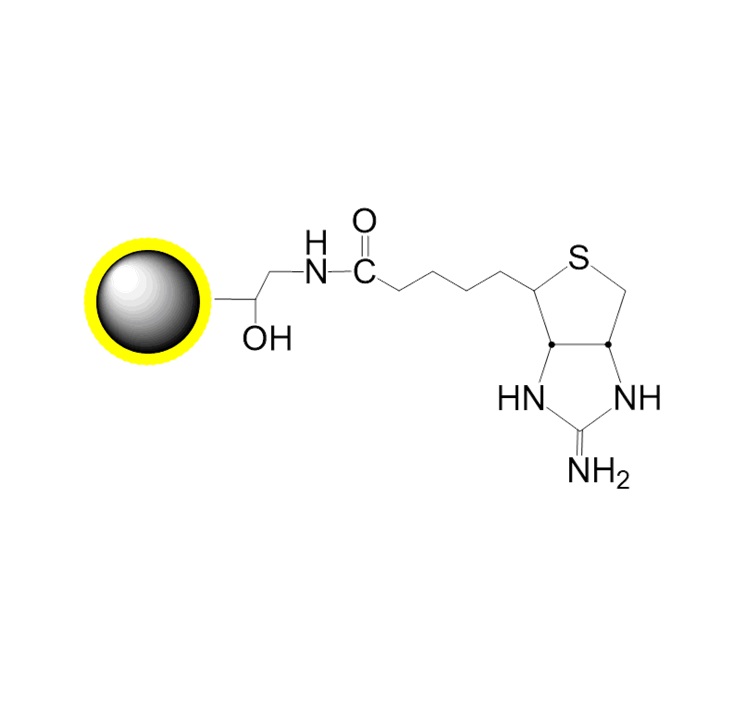
G-Iminobiotin |
PMG102-2 |
2 ml |
|
PuriMag? G-Iminobiotin are 2-iminobiotin-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles designed for magnetic isolation of avidin-, neutravidin-, or streptavidin-labeled components. These beads feature a large surface area and deliver high capture efficiency in affinity-based separations.
Key Binding Properties:
Operational Advantage:
Biotin-Avidin/Streptavidin Interaction:
Extremely strong binding (KD ≈ 10-15 M)
Requires harsh elution conditions (6M guanidine HCl, pH 1.5), causing irreversible protein denaturation.
Iminobiotin Specificity:
pH-dependent binding affinity:
High pH (11-12): KD = 3.5 × 10-11 M (deprotonated iminobiotin: >C=NH)
Low pH (3-4): KD < 10-3 M (protonated iminobiotin: >C=NH2+)
Gentle elution at pH ~4 using acetate buffer protonates iminobiotin, releasing streptavidin-tagged proteins while preserving functionality of conjugated biomolecules. This contrasts with conventional biotin systems requiring denaturing conditions.
2. product description
Product Specifications
Description
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles
Particle Size
200 nm
Number of Beads
~1.7×1010 beads/mg
Matrix
Proprietary polymer
Functional group
Streptavidin group
Group density
~150 μmol iminobiotin / g Beads
Binding capacity
≥30 μg streptavidin / mg Beads
Magnetization
60~70 EMU/g
Formulation
10mg/mL in 0.5 M NaCl, 0.01 M sodium phosphate, pH 6.8, containing 0.02% sodium azide
Storage
1 year at 2~8 ℃. Do not freeze.
3. Instructions for Use
A. Buffers (Not Provided)
1.Binding/Wash Buffer: 50 mM Ammonium Carbonate or Sodium Borate, pH 11.0, containing 0.5 M NaCl.
2.Elution Buffer: 50 mM Ammonium Acetate or Sodium Acetate, pH 4.0.
B. Separation Procedure
1.Aspirate 50 μL (0.5 mg) of magnetic beads. Add 1 mL of Binding Buffer to wash the beads per sample.
2.Separate magnetically for 2 minutes or until the supernatant is clear.
3.Aspirate and discard the supernatant. Add 1 mL of Binding Buffer and wash again.
4.Repeat step 2. Remove and discard the supernatant.
5.Resuspend the beads in 450 μL of Binding Buffer.
6.Add 50 μL of serum or cell culture supernatant to the beads.
Note: Sample volume can be modified according to user preference. If the volume of sample supernatant is <500 μL, dilute it to a final volume of 500 μL using Binding Buffer.
7.Mix gently for 30 minutes using a vortex mixer or rotator.
8.Separate magnetically for 2 minutes or until the supernatant is clear using a magnetic separator.
9.Remove and discard the supernatant.
10.Add 500 μL of Binding Buffer to wash the beads and remove unbound proteins.
11.Repeat steps 8 and 9 again. Remove the supernatant.
12.Add 100 μL of Elution Buffer to the beads and mix thoroughly.
13.Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes, with occasional gentle agitation or vortexing.
14.Desalt or dialyze the eluted sample to transfer it into a suitable buffer.
C. Notes
Analogous to the elution of immobilized avidin and 2-iminobiotin or its conjugates, the use of 0.1% (w/v) Triton X-100, Tween 80, or Sodium Deoxycholate may not interfere with the affinity separation. However, the use of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) completely disrupts all binding.
Horseradish Peroxidase and Alkaline Phosphatase conjugates of Avidin/Streptavidin can also be purified using 2-Iminobiotin magnetic beads. Equilibrate the beads at pH 10 instead of pH 11 and achieve specific elution using a pH 6.0 buffer.
In the analogous systems mentioned previously, specific elution was achieved using either a pH 4.0 buffer or 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) containing 1 mM Biotin. The advantage of this approach is the requirement for a less acidic buffer, but the disadvantage is that biotin binds selectively (essentially permanently) to the avidin beads, displacing the iminobiotin analog.
Iminobiotin magnetic beads can be regenerated by washing with pH 11.0 buffer, and then stored at 0-8°C in a pH 7.0 buffer containing 0.5 M NaCl and a suitable preservative.
(These magnetic beads are for research use only!)