|
Ordering information |
|||
|
Name |
Cat. No. |
Vol. |
Scheme |
|
GS-Epoxy (5 C spacer) |
PMG001-2 PMG001-5 |
2ml 5ml |
|
|
GL-Epoxy (15 C spacer) |
PMG002-2 PMG002-5 |
2ml 5ml |
|
1. Overview
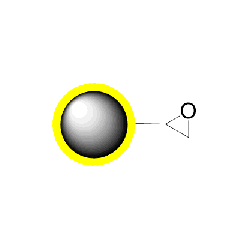
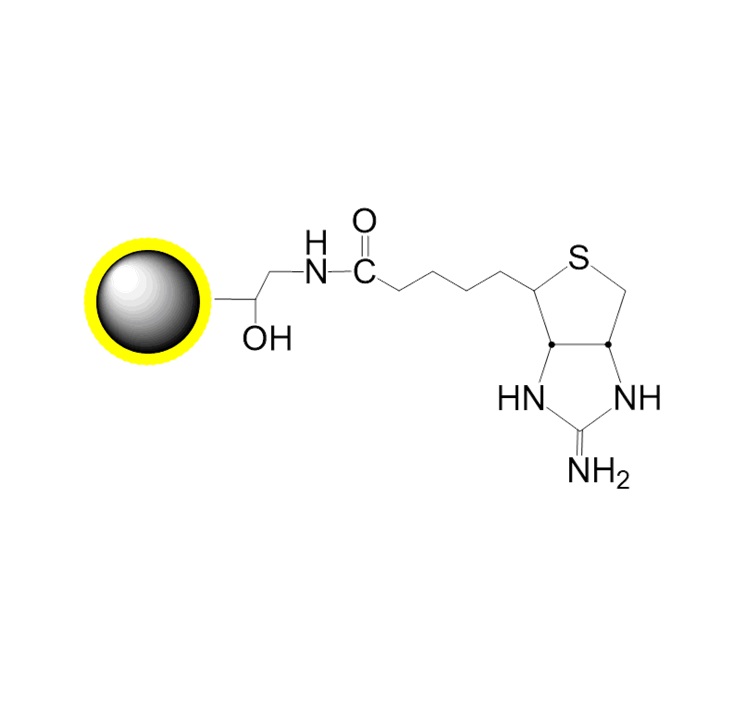
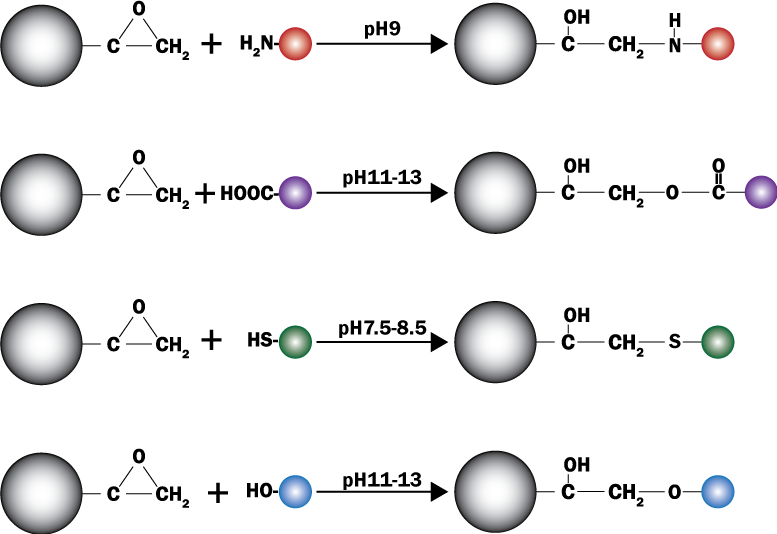
PuriMag? G-Epoxy Epoxy-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles are pre-activated, uniform, polymer-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. The beads feature a surface coated with a high density of epoxy functional groups, designed for covalent binding to ligands containing amines, thiols, or hydroxyl groups.
Binding Conditions:
Hydroxyl-containing ligands: pH 11–12
Amine-containing ligands: pH > 9
Thiol-containing ligands: pH 7.5–8.5
Water-insoluble ligands may be coupled in organic solvents (Dioxane, DMF, DMSO). Epoxy-activated beads are optimal for coupling large proteins.
Features & Advantages:
Pre-activated for immediate use
Efficient covalent coupling at pH 9–12, 20–40°C for 16–24 h
Stable covalent bonds with minimal ligand leaching
Creates reusable immunoaffinity matrices
Low non-specific binding
Immobilization capacity: 1–30 mg protein or 0.1–3 mg peptide per gram beads
Applications:
Cell sorting, immunoprecipitation, purification of antibodies, proteins/peptides, DNA/RNA
Schematic of Coupling Mechanism:
2. product description
|
Product Specifications |
|
|
Description |
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles |
|
Particle Size |
200 nm |
|
Number of Beads |
~1.7×1010 beads/mg |
|
Matrix |
Proprietary polymer |
|
Functional group |
Epoxy group |
|
Group density |
~300 μmole / g of Beads |
|
Magnetization |
60~70 EMU/g |
|
Formulation |
10 mg/ml suspension in alcohol |
|
Stability |
pH 3.5~10, 4~80 ℃, most organic solvents |
|
Storage |
1 year at 2~8 ℃. Do not freeze. |
3. Instructions for Use
Note: The following protocol is an example for coupling amine-containing ligands to PuriMag? Epoxy-Activated Magnetic Nanoparticles.
Optimization of bead quantity for specific samples is strongly recommended. Insufficient ligand loading may increase non-specific binding, while excessive loading may cause steric hindrance. For affinity matrices, use 1–30 mg protein or 0.1–3 mg peptide per gram beads. Scale protocol proportionally as needed.
A. Required Materials
Magnetic Racks: For 2×50 mL or 2×15 mL tubes (e.g., Mrack03); For 12×1.5–2 mL tubes (e.g., Mrack02)
Coupling Buffer: 0.1 M Sodium Carbonate or 0.1 M Sodium Phosphate, pH 8.5–10
Note: Minimal ionic strength is critical. Buffer must NOT contain amines (e.g., Tris), thiols, hydroxyls, or phenols. Wash/storage buffers may contain these.
Blocking Buffer: 1 M Ethanolamine, pH 9.0
Wash Buffer: PBS, pH 7.4
B. Coupling Protocol
*Note: PuriMag? Epoxy Beads are supplied as 10 mg/mL suspension in ethanol. Store at 4°C. Vortex before use.*
1.Transfer 2 mg beads to microcentrifuge tube.
2.Place tube on magnetic rack for 1 min. Remove supernatant. Resuspend beads in 50 μL coupling buffer.
3.Repeat Step 2 three times.
*Note: Use hydrated beads immediately.*
4.Dissolve protein/peptide in 50 μL coupling buffer.
*Note: Optimize concentration empirically. Recommended: 1–10 mg/mL for proteins; >200 μmol/mL for small peptides.*
5.Add protein solution to washed beads. Resuspend and incubate.
*Note: Amine ligands (proteins): 15–48 h at 25°C (or 48–72 h at 4°C for sensitive ligands). Peptides/hydroxyl/thiol ligands: 4–15 h at 25–75°C.*
6.Wash beads 3× with 1 mL PBS.
7.Add 0.5–1 mL blocking buffer. Incubate ≥4 h or overnight at 4°C.
8.Wash beads 4–6× with 1 mL PBS.
9.Resuspend in PBS with 0.1% sodium azide. Store at 2–8°C (avoid freezing).
C. Coupling Efficiency Optimization
C-1. Ligand Loading Optimization
Ligand coupling increases linearly with concentration until saturation, then plateaus. Test 1–10 mg ligand per gram beads for optimal density.
C-2. Buffer & pH
Use 10 mM buffer strength for pH control. Suitable buffers: Carbonate, Borate, Phosphate. Avoid Tris, glycine, or nucleophiles. Optimal coupling pH:
Hydroxyl ligands: pH ~13
Amine/thiol ligands: pH 9–13
*Note: Higher pH accelerates reaction but promotes epoxy hydrolysis.*
C-3. Temperature & Duration
Standard: Overnight at 20°C. For stable ligands, increase temperature (≤40°C) to reduce time. Minimize duration to prevent ligand degradation.
C-4. Blocking & Washing
1.Block residual groups with 1M ethanolamine (pH 8–9, 4 h).
2.Wash thoroughly with coupling buffer.
3.Remove ionically-bound ligands by alternating washes:
Acidic: 100 mM acetate + 500 mM NaCl, pH 4.0
Basic: 100 mM PBS + 500 mM NaCl, pH 8.0
D. General Affinity Purification Protocol
Note: While nucleic acid purification is straightforward, protein purification requires target-specific optimization.
1.Transfer optimized bead amount to tube. Separate magnetically (1–3 min). Discard supernatant.
*Note: Titrate beads against target abundance. Typical binding: 1–20 μg target protein per mg beads.*
2.Wash beads 3× with 5 bead volumes PBS (30 sec resuspension per wash).
3.Incubate beads with crude sample containing target (1–2 h at RT or optimized temperature).
4.Wash with PBS or 1M NaCl until eluate OD??? < 0.05.
5.Elute target using: Low pH (2–4); High pH (10–12); High salt; Heat; Affinity elution; Boiling in SDS-PAGE buffer
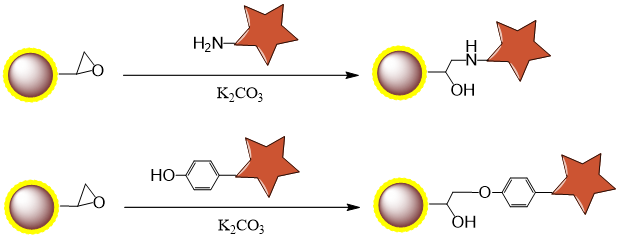
Appendix: Immobilization of Small Molecule Compounds Containing Phenol or Primary Amine Groups onto Epoxy Magnetic Beads in Organic Phase
For screening purposes, initial optimization of ligand loading density on the beads is essential. Varying ligand concentration allows control over immobilization density. This protocol demonstrates ligand immobilization at four concentrations (0 mM, 2 mM, 10 mM, and 50 mM) on epoxy beads.
1. Materials
1.1 Beads & Ligand
PuriMag? G-Epoxy Beads: 10 mg (Functional group density: ~200 nmol/mg)
Ligand: ~30 mg
1.2 Reagents
N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF): 15 mL
Potassium carbonate (K?CO?), M.W. 138.21: 50 mg
Methanol (MeOH): 7 mL
1.3 Equipment
Centrifuge, Vortex Mixer, Rotating Mixer, Ultrasonic Disperser, Magnetic Stand
2. Method
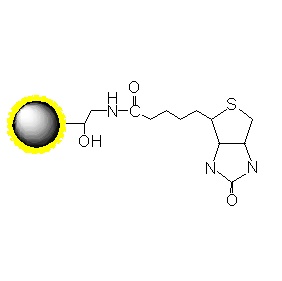
2.1 Binding Mechanism
2.2 Procedure
1.Prepare 1 mL of 50 mM ligand solution in DMF.
2.Aliquot 2.5 mg epoxy beads into four 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes.
3.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
4.Add 500 μL DMF, disperse beads via ultrasonication.
5.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
6.Repeat steps 4-5 twice more (total 3 washes).
7.Add DMF and prepared ligand solution. Disperse beads via ultrasonication.
Concentration (mM)
0
2
10
50
Epoxy beads (mg)
2.5
2.5
2.5
2.5
DMF (μl)
500
480
400
0
50 mM ligand (μl)
0
20
100
500
Potassium carbonate (mg)
0
1.4
7
35
Total (μl)
500
500
500
500
*Note: Add ligand solution after DMF to prevent localized high concentration.*
8.Add 10 molar equivalents K?CO? to ligand (e.g., 35 mg K?CO? for 50 mM ligand). Mix via ultrasonication.
(Alternatively: Pre-weigh K?CO? in separate tube before adding ligand/beads)
9.React at 60°C for 16–20 h (overnight) with vortex mixing in incubator.
(K?CO? will remain undissolved)
10.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
11.Add 500 μL 50% DMF, disperse beads via ultrasonication.
12.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
(If beads aggregate at solution interface, discard only upper layer)
13.Repeat steps 11-12 once more (total 2 washes).
14.Add 500 μL ultrapure water, disperse beads via ultrasonication.
15.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
16.Add 500 μL 50% MeOH, disperse beads via ultrasonication.
17.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
18.Repeat steps 16-17 twice more (total 3 washes).
19.Resuspend in 100 μL 50% MeOH. Store at 4°C.
(Ligand-immobilized bead concentration: 0.5 mg/20 μL)